Home Improvement: 7 Toxic Chemicals Hiding In Your Home And How To Reduce Exposure
Your home can be your safe haven from all the germs and bacteria that you encounter in public places. When it comes to safeguarding your health, even the toughest antiseptics and antibacterial cleansers could actually be hurting, not helping. While cleanliness and good hygiene is a preventive measure of sickness and disease, your health is at risk due to the exposure of a number of toxic chemicals hiding in the home.
The nonprofit Environmental Working Group (EWG) has found more than 80,000 chemicals are used in everyday goods, and each year, an estimated 2,000 new ones are introduced for use in such everyday items as foods, personal care products, prescription drugs, household cleaners, and lawn care products. These chemicals can be hiding in your bathroom cabinet, under your sink, laundry supplies, and through every square inch of your home. You can renovate your home and do some home improvement by identifying these seven harmful chemicals, their effects, and what you can do to reduce your exposure.
An infographic by Body Logic MD and Owain Lloyd-Williams, a UK-based writer and creative content author on behalf of BodyLogic MD can be found below.
1. Bisphenol A (BPA)
What It Is:
BPA is a common food contaminant used to make polycarbonate and epoxy resins, two common synthetics used for food and drink containers and the linings for food and beverage cans, and coating on receipts.
What It Does:
The chemical is a synthetic estrogen that can disrupt the endocrine system, according to the EWG, that has been linked to a wide variety of ills such as infertility, breast and reproductive system cancer, and behavioral changes in children, among many others.
How To Reduce Exposure:
You can avoid BPA by choosing fresh, frozen, or even homemade versions of canned foods. It’s best to limit your consumption of canned food, particularly if you are pregnant. You can also say “no, thanks” when your cashier asks if you would like a receipt.
2. Dioxins
What It Is:
This is a family of toxic chemicals that share a similar chemical structure and induce harm through a similar mechanism. Incineration of waste produces high levels of dioxins along with the bleaching of paper and wood pulp.
What It Does:
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has characterized this chemical as likely human carcinogens that are expected to increase the risk of cancer. It can lower sperm quality and damage the immune and reproductive system.
How To Reduce Exposure:
The most simple way to avoid dioxins is to cut back on your consumption of fatty meat and dairy products. You should also avoid chlorine-based bleach and bleached paper products, such as disposable diapers and toilet paper.
3. Flame Retardants
What It Is:
Chemical fire retardants are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, to meet flammability standards. Although not all flame retardants present concerns, these types do: halogenated flame retardants and organophosphorous flame retardants. They contain chlorine or bromine, and phosphorous bonded to carbon, respectively.
What It Does:
These toxic chemicals are known for their impact on thyroid hormones disruption, female infertility, and can lower sperm count. According to EWG, one class of flame retardants called polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), have been taken off the market due to toxicity concerns but have been replaced with “chlorinated tris” (TDCIPP) and chemical mixtures such as Firemaster® 550. However, these chemicals can lead to deficits in motor skills, learning memory, and behavior in children.
How To Reduce Exposure:
Fire retardants can be found in furniture, carpet padding, and even in some baby pillows. You can reduce exposure by dusting and using a heap filter vacuum cleaner, since they tend to bind to dust. Using a face mask when cleaning carpets is also advised.
4. Lead
What It Is:
This chemical is a naturally occurring element found in small amounts in the earth’s crust, says the EPA. Lead is found in the air, the soil, the water, and even inside your home. Lead and lead compounds are widely used in a variety of products found in the home such as paint, ceramics, pipes and pluming materials, solders, gasoline, batteries, ammunition, and cosmetics.
What It Does:
Chronic exposure to lead can lower IQ and lead to brain damage, cause hearing and vision impairment, disrupt hormonal development in fetuses and premature birth, and lower sperm count. Lead is toxic to everyone, but unborn babies and young children are at risk for health problems because they’re smaller, growing bodies are more susceptible to absorbing and retaining lead. It can act like a poison when absorbed by the skin.
How To Reduce Exposure:
Lead can show up in water, so it’s best to get a lead-removing water filter. It’s best to avoid old paint that is chipped to crumbling. To avoid lead found in soil, don’t wear outdoor shoes indoors.
5. Organophosphate Pesticides
What It Is:
These organophosphate-based pesticides are used as a form of agricultural insecticide in the U.S. on fruits and vegetables. The breakdown of OP pesticides occurs when they are exposed to light and air. However, it is not known whether they ever degrade fully, says the Center for Environmental Research and Children's Health at UC Berkeley, School of Public Health.
What It Does:
OP pesticides chronic exposure has been linked to Parkinson’s Disease, neurotoxic effects, decrease in male testosterone, and linked to a variety of cancers. This is a common but deadly pesticide.
How To Reduce Exposure:
Eating organic can help reduce the presence of this insectide. Organic farmers do not use synthetic pesticides like organophosphates on their fields. If you can’t go organic, it’s best to dry your produce with a clean towel or paper towel to remove remaining pesticide residues. Also, remember to throw away the outer layers of leafy vegetables like lettuce or kale.
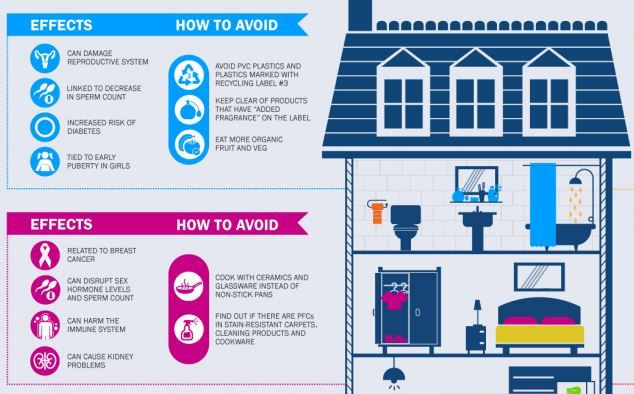
6. Perfluroinated Chemicals (PFCs)
What It Is:
PFCs are fluorine-containing chemicals that make materials stain- and stick-resistant. They break down very slowly in the environment and are often characterized as persistent, according to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. PFCs may be used to keep food from sticking to cookware, make sofas and carpets resistant to stains, male clothes and mattresses more waterproof, and sometimes they’re used in food packaging, including some firefighting materials. These large group of manufactured compounds are used in aerospace, automotive, building and construction, and electronics since they can help reduce friction.
What It Does:
PFCs have been associated with breast cancer, disrupting sex hormone levels and sperm count, harm the immune system, and cause kidney problems.
How To Reduce Exposure:
Cooks can reduce exposure by using ceramics and glassware instead of non-stick pans. You can look is there are any PFCs in stain-resistant carpets, cleaning products and cookware.
7. Phthalates
What It Is:
Phthalates are a group of chemicals used as plasticizers that provide flexibility and durability to plastics such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), according to EPA. They are commonly used in applications that include building materials, clothing, cosmetics, perfumes, food packaging, toys, and vinyl products –flooring, shower curtains, and rain coats. These chemicals are also used in medical applications like blood transfusion bags and tubing, intravenous fluid bags and tubing, and other medical devices.
What It Does:
They can damage the reproductive system, decrease sperm count, increase diabetes risk, and can induce early puberty in girls.
How To Reduce Exposure:
You can avoid phthalates by not using PVC plastics and plastics marked with recycling label #3. Steer clear of products that have “added fragrance” on the label. Also, eat more organic fruits and vegetables.



























